Zhejiang Wenxian Gear Co., Ltd. | [email protected]
China high quality Customied Cylinderical Shaft Module6 with 54 Teeth Customized for Truck/ Construction Machinery/ Oil Drilling Rig spurs gear
Product Description
Product introduction
| Gear model | Customized gear shaft accoding to customers sample or drawing |
| Processing machine | CNC machine |
| Material | 20CrMnTi/ 20CrMnMo/ 42CrMo/ 45#steel/ 40Cr/ 20CrNi2MoA |
| Heat treattment | Carburizing and quenching/ Tempering/ Nitriding/ Carbonitriding/ Induction hardening |
| Hardness | 58-62HRC |
| Qaulity standerd | GB/ DIN/ JIS/ AGMA |
| Accuracy class | 5-8 class |
| Shipping | Sea shipping/ Air shipping/ Express |
Factory introduction
ZheJiang Yingxing Gear Co., LTD is set product development, production and sales of specialized enterprises, the company was founded in 2007, is located in Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Bridge River, 50 kilometers from the provincial capital HangZhou city, convenient transportation.
The company has modern professional production workshop covers an area of 30,000 square meters, 120 employees, including professional and technical staff of 30 people. We buy the advanced processing center equipment from Germany and American. We produce the gear for reducer,agricultural machinery, construction machinery, oil drilling rig,and other aspects of the production. The company has been appraised as ZheJiang quality products, corporate credit quality units. The company has offices in HangZhou.
Our products sell well in China and exported to Europe, the Americas, the Middle East, Southeast Asia and other countries. My company adhered to the “good faith, winning by quality, first-class service will be presented to our customers” for the purpose, we are willing to be honest with you, and work together for a better tomorrow.
Factory pictures and cerfitication
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Oil Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spiral Gear |
| Material: | 20crmnti |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
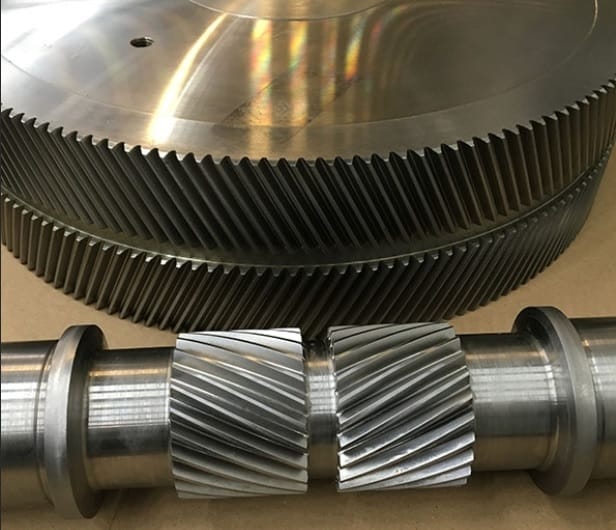

What is the purpose of using helical gears in power transmission?
Helical gears are commonly used in power transmission systems for various purposes. Here’s a detailed explanation of the purpose and advantages of using helical gears in power transmission:
- Smooth and Efficient Power Transfer: One of the primary purposes of using helical gears in power transmission is to achieve smooth and efficient transfer of power. The inclined tooth profile of helical gears allows for gradual and continuous engagement of teeth, minimizing shock loads and ensuring a more uniform distribution of force. This results in smoother power transmission with reduced noise, vibration, and wear.
- High Torque Transmission: Helical gears are known for their high torque-carrying capacity. The inclined teeth of helical gears enable a larger tooth contact area compared to other gear types such as spur gears. This increased tooth contact area allows helical gears to transmit higher torque, making them suitable for applications that require the transfer of large amounts of power, such as in industrial machinery, automotive drivetrains, and heavy-duty equipment.
- Variable Speed Ratios: Helical gears can be designed with different numbers of teeth and varying helix angles, allowing for a wide range of speed ratios. By selecting the appropriate combination of gears, the rotational speed and torque can be adjusted to meet the requirements of the power transmission system. This flexibility in speed ratios makes helical gears versatile in applications where variable speed control is necessary.
- Reduction of Noise and Vibration: The inclined tooth profile and gradual engagement of helical gears contribute to the reduction of noise and vibration in power transmission systems. Compared to spur gears, helical gears generate less noise and vibration due to their smoother meshing characteristics and improved load distribution. This makes helical gears particularly beneficial in applications where noise reduction and smooth operation are important considerations, such as in automotive transmissions and precision equipment.
- Compact Design: Helical gears can achieve high gear ratios within a relatively compact design. The inclined teeth of helical gears allow for more teeth to be in contact at any given time, enabling a higher gear ratio compared to spur gears of the same size. This compactness is advantageous when there are space constraints or when a smaller gear mechanism is desired without sacrificing performance or torque capacity.
- High Reliability and Durability: Helical gears are designed to distribute the load over multiple teeth, resulting in improved load-carrying capacity and enhanced gear strength. The inclined tooth profile allows for a larger contact area, reducing stress concentrations and increasing the gear’s resistance to wear and fatigue. These factors contribute to the high reliability and durability of helical gears, making them suitable for demanding power transmission applications that require long service life.
In summary, the purpose of using helical gears in power transmission is to achieve smooth and efficient power transfer, high torque transmission, variable speed control, noise and vibration reduction, compact design, and high reliability. These advantages make helical gears widely used in various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, energy, and many other applications that require reliable and efficient power transmission.
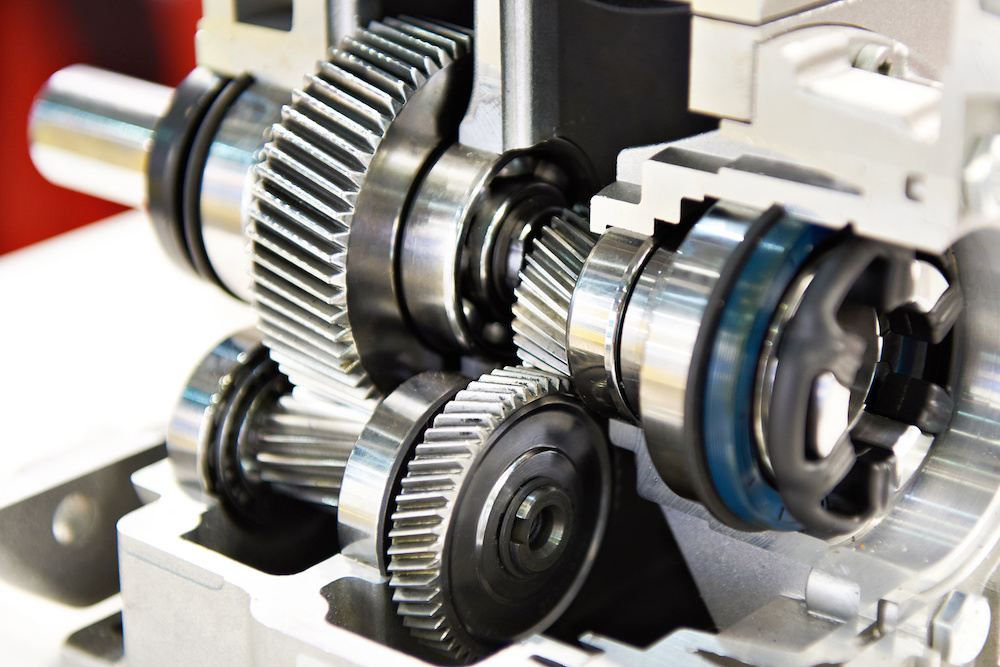
How do you address noise and vibration issues in a helical gear system?
In a helical gear system, addressing noise and vibration issues is crucial to ensure smooth and quiet operation, minimize component wear, and enhance overall system performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to address noise and vibration issues in a helical gear system:
- Proper Gear Design: The design of the helical gears can significantly impact noise and vibration levels. Design considerations such as the helix angle, tooth profile modification, and gear tooth contact pattern optimization can help minimize gear noise and vibration. A well-designed gear system with proper tooth geometry and accurate alignment reduces the likelihood of gear meshing irregularities that contribute to noise and vibration.
- Precision Manufacturing: High-quality manufacturing processes are essential to minimize noise and vibration in helical gear systems. Precise gear cutting techniques, such as hobbing or grinding, ensure accurate tooth profiles, which help reduce gear meshing deviations and associated noise. Additionally, maintaining tight manufacturing tolerances and surface finishes on gear components can help minimize vibration caused by irregularities or imperfections.
- Alignment and Assembly: Proper alignment and assembly of the helical gears are critical to minimize noise and vibration. Ensuring precise alignment of the gear shafts and gear meshing is essential to achieve optimal contact between the gear teeth. The use of alignment tools, such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems, can aid in achieving accurate alignment. Additionally, proper assembly techniques, including appropriate gear backlash and preload adjustment, can help minimize noise and vibration by optimizing gear meshing conditions.
- Optimal Lubrication: Proper lubrication is vital for reducing noise and vibration in a helical gear system. Adequate lubrication creates a thin film between the gear teeth, minimizing friction and wear. The lubricant also helps to dampen vibrations and dissipate heat generated during gear operation. Using the correct lubricant type, viscosity, and maintaining proper lubricant levels are essential for noise and vibration control.
- Stiffness of Gearbox Housing: The stiffness and rigidity of the gearbox housing influence noise and vibration levels in a helical gear system. A robust and well-designed housing structure helps to minimize the transmission of vibrations from the gears to the surrounding environment. It is important to ensure that the gearbox housing is adequately braced and supported to reduce resonances and vibrations that can contribute to noise.
- Vibration Damping: Implementing vibration damping techniques can help mitigate noise and vibration in a helical gear system. This can include the use of vibration-absorbing materials, such as elastomers or damping pads, at appropriate locations within the gear system. These materials help absorb and dissipate vibrations, reducing noise transmission and minimizing gear system resonance.
- Condition Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular condition monitoring and maintenance practices are essential for identifying and addressing noise and vibration issues in a helical gear system. Periodic inspections, including vibration analysis, can detect any abnormal vibration patterns or wear indications. Timely maintenance, such as addressing misalignment, worn components, or inadequate lubrication, can prevent further deterioration and reduce noise and vibration levels.
By implementing these measures, engineers can effectively address noise and vibration issues in a helical gear system, resulting in quieter operation, reduced component wear, and improved overall system performance.
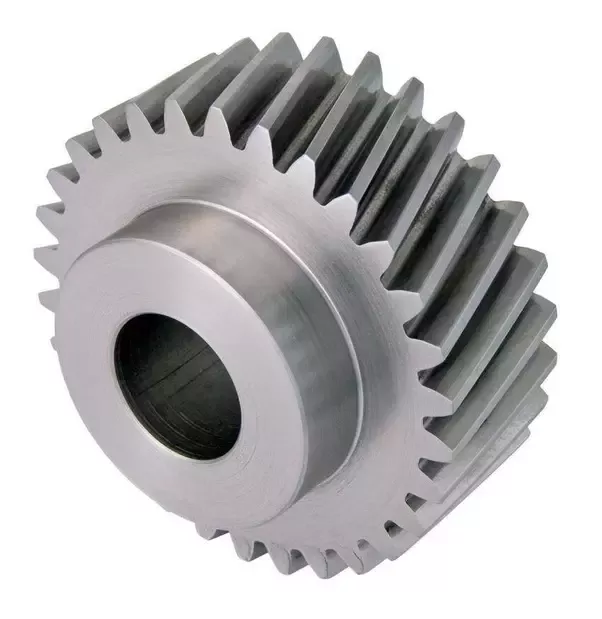

Can you explain the concept of helical gear teeth and their orientation?
The concept of helical gear teeth and their orientation is essential to understanding the design and operation of helical gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of helical gear teeth and their orientation:
A helical gear consists of teeth that are cut in a helical pattern around the gear’s circumference. Unlike spur gears, which have teeth that are perpendicular to the gear axis, helical gears have teeth that are angled or inclined with respect to the gear axis. This inclination gives the teeth a helix shape, resulting in the name “helical” gears.
The orientation of helical gear teeth is defined by two main parameters:
- Helix Angle: The helix angle represents the angle formed between the tooth surface and an imaginary line perpendicular to the gear axis. It determines the degree of inclination or spiral of the gear teeth. The helix angle is typically measured in degrees. Positive helix angles indicate a right-hand helix, where the teeth slope in a right-hand direction when viewed from the gear’s end. Negative helix angles represent a left-hand helix, where the teeth slope in a left-hand direction. The helix angle affects the gear’s performance characteristics, including tooth engagement, load distribution, and axial thrust.
- Lead Angle: The lead angle is the angle formed by the helical tooth and a plane perpendicular to the gear axis. It represents the angle of advance of the helix over one revolution of the gear. The lead angle is equal to the helix angle divided by the gear’s number of teeth. It is commonly used to define the helical gear’s size and pitch.
The helical tooth orientation offers several advantages over spur gears:
- Smooth and Quiet Operation: The helical shape of the teeth allows for gradual engagement and disengagement during gear rotation. This results in smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears, which often produce noise due to the sudden contact between teeth.
- Increased Load-Carrying Capacity: The helical tooth design provides a larger contact area between meshing gears compared to spur gears. This increased contact area allows helical gears to transmit higher loads and handle greater torque without excessive wear or tooth failure.
- Load Distribution: The helical orientation of the teeth enables load distribution along the tooth face. Multiple teeth are engaged simultaneously, distributing the load across a broader surface area. This characteristic helps minimize stress concentrations and increases the gear’s durability.
- Axial Thrust Load: The helical tooth engagement introduces axial forces and thrust loads along the gear axis. These forces must be properly supported and managed in the gear system design to ensure smooth operation and prevent excessive wear or failure.
The design and manufacturing of helical gears require specialized cutting tools and machining processes. The helical teeth are typically generated using gear hobbing or gear shaping methods. The tooth profile is carefully designed to ensure proper meshing and minimize noise, vibration, and wear.
In summary, helical gear teeth have a helical or spiral shape, which distinguishes them from the perpendicular teeth of spur gears. The orientation of helical gear teeth is defined by the helix angle and lead angle. Helical gears offer advantages such as smooth operation, increased load-carrying capacity, load distribution, and axial thrust load. These characteristics make helical gears suitable for applications that require efficient power transmission, precise motion control, and reduced noise and vibration.


editor by Dream 2024-05-07
